Introduction
About
- Data Protection and Privacy
- Access Control
- Policy Languages, Models, and Standards
Course Objectives
Understand the relevance of data protection A detailed understanding of the most important access control models Knowledge of the well-established privacy principles Ability to specify access control and privacy policies Ability to evaluate access control and privacy policies
Topics covered
- Access Control
- Usage Control
- Privacy-aware Access Control
- eXtensible Access Control Markup Language(XACML)
- A taste of research
Outline
- Defining Privacy
- Privacy Threatss
- Appliaction
- Location-based services
- RFID
- Social Networks
- Privacy Enhancing Technologies
Defining Privacy
Abstract and subjective concept, hard to define-->Dependent on cultural issues, study discipline, stakeholder, context
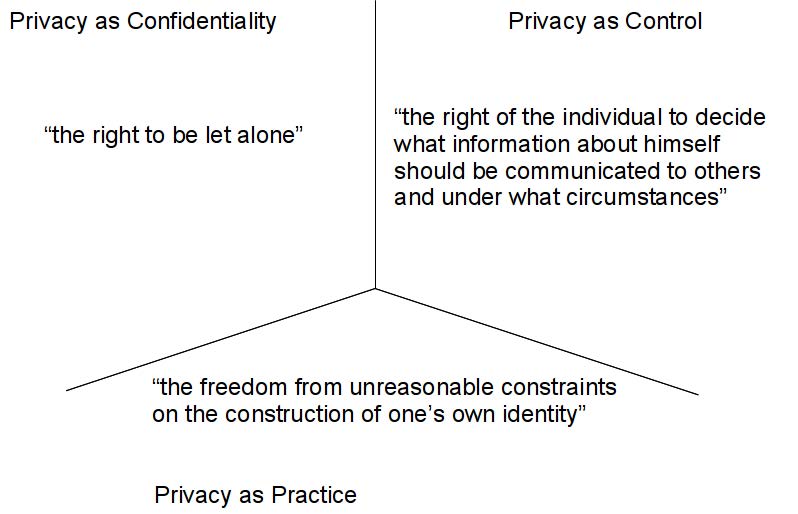
Popular definitions:
- (Privacy as Confidentiality)“The right to be let alone” (Brandeis & Warren, 1890)-->Focus on freedom from intrusion
- (Privacy as Control)“The right of the individual to decide what information about himself should be communicated to others and under what circumstances”(Westin, 1967)-->Focus on control/Focus on information self-determination
- (Privacy as Practice)“The freedom from unreasonable constraints on the construction of one’s own identity” (Agre, 1999)-->Focus on autonomy
Privacy Paradigms
What Privacy is About
- Privacy concerns personal information
- Privacy is more than confidentiality (机密性)
- Freedom from intrusion(闯入;打扰;(对某事的)干扰, 干涉)
- Control of informationn about oneself
- Autonomy(自治,自治权)
Privacy Threats
How much privacy do we have left?
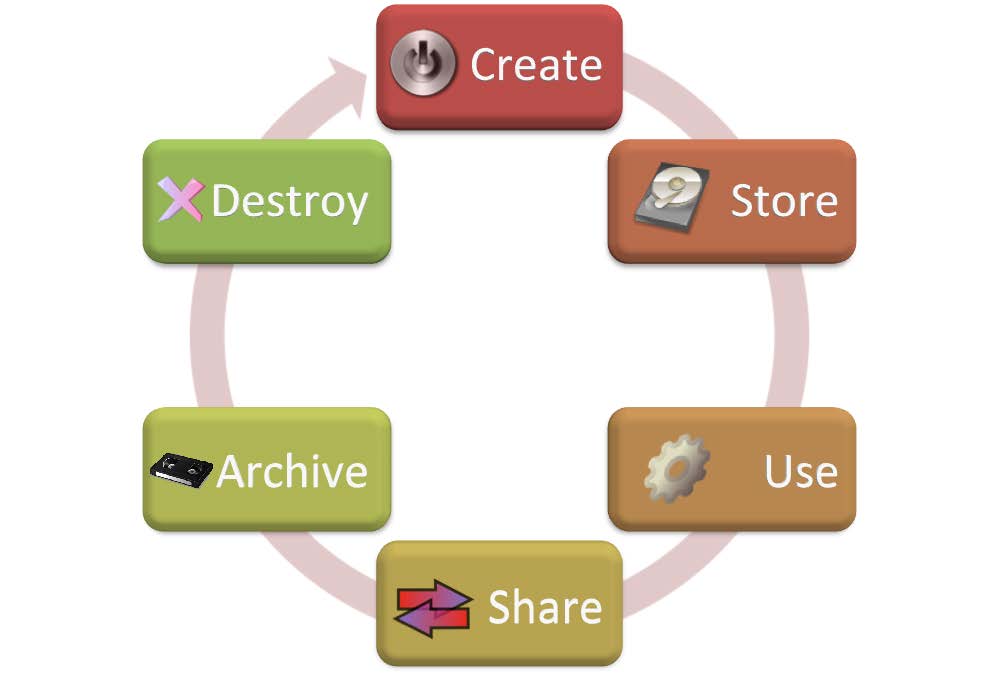
Data Life Cycle
Taxonomy(分类学,分类系统) of Privacy Threats(Solove)
- Information collection
- surveillance(监视)
- interrogation(讯问(审问)的行为实例;讯问(审问)过程,疑问句;问题)
- Information processing
- aggregation(聚集,集成;集结;聚集体,集成体)
- identification
- insecurity
- secondary usage
- exclusion
- Information dissemination(散播;宣传)
- breach(破坏, 违反;破裂, 不和;缺口, 裂口;攻破;破坏, 违反) of confidentiality
- disclosure
- exposure
- increased accessibility
- blackmail
- appropriation(拨付,拨发;拨款;占用,挪用,盗用)
- distortion(曲解;失真)
- Invasion(侵犯;入侵,侵略;侵袭)
- intrusion
- decision interference(干涉, 介入;阻碍, 干扰)
Secondary Usage
Use information for a purpose other than the one for which it was obtained
- Use of customer information for marketing
- Sale(or trade) of consumer information to other businesses
- Government agencies' use of consumer database
Aggregation
Combining and comparing information from more than one database
- Why aggregation is a problem? Data already in the system
- Individual pieces of data may be not very telling
But when combined together, they may reveal(显示; 露出;泄露; 透露) more information about a person
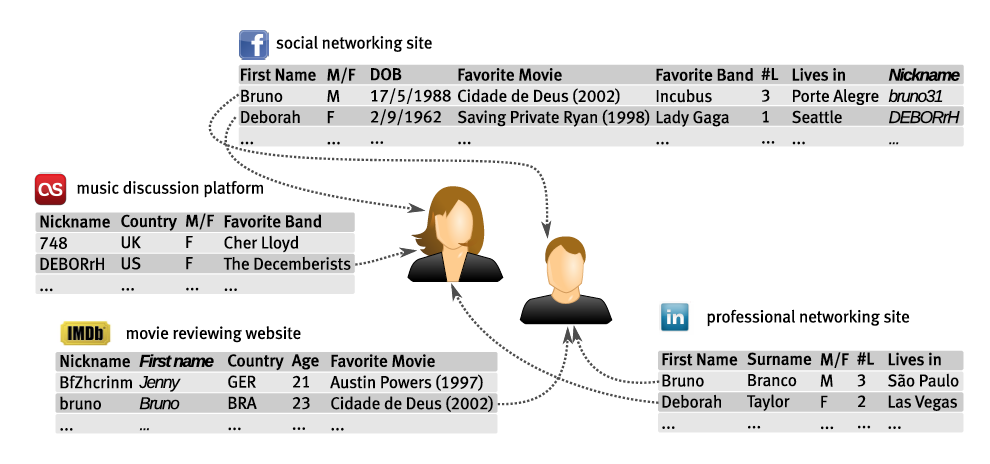
Aggregated information about a person is often used to judge her
- Amazon.com uses aggregated data about book-buying history to recommend other books
- Sharing of government agencies’ databases to detect frauds
- Insurance companies can make decisions based on information of diseases, lifestyles, etc.
- Aggregations of credit reports used to evaluate a person’s financial reputation for granting loans
Video Surveillance
CCTV monitoring at public places(airports, malls,...)
Other Threats
- Invisible Information Gathering
- Satellite surveillance
- Loyalty cards(e.g., supermarket club cards)
- Web-tracking data; cookies
- ISPmonitoring
- Your ISP "knows" every site you visit
- Google stores your search history
- Profiling 例子17页
- Use of customer preferences to predict behaviors of people
- Profiling customers to determine their propensity(倾向;习性) toward a product/service
- Government agencies create descriptions of possible terrorists
- Identity Theft
- Discrimination (propensity)
Why now?
Computers not needed for the invasion of privacy
Digitization of information make it possible to
- collect and store massive amout of personal information
- correlate information from different sources
access information on the network locally or remotely
Computers simply make new threats possilbe and old threats more powerful
Applications
- Location-based services
- RFID
- Social Networks
How many ways can we be located today?
- cell phone (turned on?)
- laptop
- credit card at the gas station
- bank card in the ATM machine
- driving through a monitored intersection
- security camera at the supermarket
- scan badge to enter a building
- ...
Location Based Service
- location-based traffic monitoring and emergency services
- e-Call, traffic congestion control
- location/service finder:
- where is the nearest restaurants, gas station,..
- variable pricing applications
- congestion pricing
- pay-as-you-drive
- social applications
- Geotagged Twitter
- Google Latitude
Why is this a problem?
- do you want to be seen at certain location (abortion clinic, AIDS clinic, business competitor, or political headquarters)
- what can be automatically inferred about a person based on location?
- any important location...
- desk in a building
- home location
- future locations
- and even identification!
- any important location...
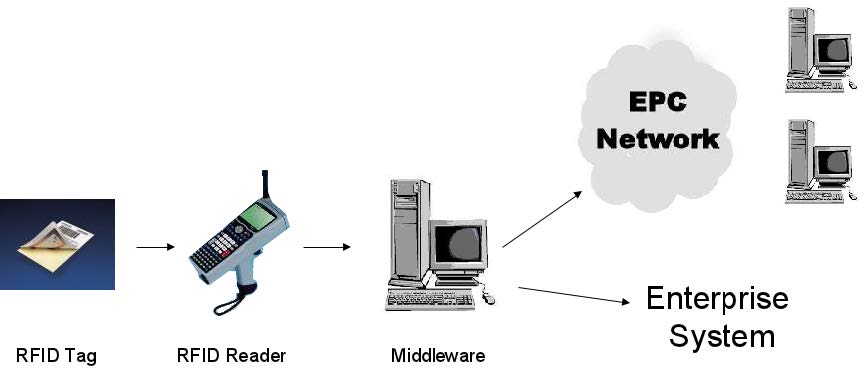
RFID Technology
- Radio Frequency Identification
- A micro-chip transmitting data when exposed to radio waves
- Conceptually similar to bar code-->used to identify and track objects of interest
RFID Data Collection Process
RFID Application
RFID From the news
2006: President of Colombia agreed to require Colombian citizens to be implanted with RFID chips before they could gain entry into the US for seasonal work.
2008: UK jails considering RFID implants for prisoners.
2015: Tenants of a hi-tech office block in Sweden implanted with RFID chips in order to gain access to the office and operate photocopiers.
RFID-Privacy Issues
- Traceability
- Disclosure of embarrassing information
- Discrimination
- Target by muggers
- ...
Social Networks
Many people publish their personal information on social networks
Social Networks--Privacy Issues 见30,31,32
- Used by professors, parents, and employers
- Used by law enforcement and college administrators for disciplinary action
- Used for surveillance and data mining
- Used by merchants for marketing
- Use by other members for criminal purposes (e.g., stalking, invasion of privacy)
Privacy Enhancing Technologies
How can we protect privacy?
Scenario


Privacy as Control: Assumptions
- Collection and Processing of personal information is useful and necessary
- Search engines: historical search data helps improve search algorithms
- Hospital: health records
- Organizations have an interest in protecting user privacy
- Organization trusted to enforce user privacy preferences
- Privacy problems arise when personal information is misused
Privacy as Control: Threats
- Database of queries can be breached
- information made public
- information abused by malicious insider and sold for profit
- Query data used for illegitimate purposes
- Query data shared with other parites without user consent(e.g.,advertisers)
- Time queries are stored("right to be forgotten")
Privacy as Control: Goals
- Focus on:
- control over personal data
- compliance(服从,听从,顺从) with data protection regulations
- Providing individuals with means to control use of their information
- Information consent, privacy settings
- Providing organizations with means to
- define and enforce security and privacy policy
- prevent/detect misuse of personal information
Privacy Settings
- Allow users to specify their privacy preferences
Make it easier for users to configure their privacy setting
- privacy preference languages, e.g., APPEL, XPref
- default suites of privacy settings
privacy wizard that automate configuration of settings
NOTE: Enforcement of privacy settings is done by the organizationn
Purpose-based Access Control
- Regulate access to data
- Privacy-aware Access Control languages
- Specify which action a user can perform on a given objects
- Specify the allowed usage of data
Policy enforcement
Ensure the purpose of data access is complaint with intended purpose
NOTE: No control after disclosure of data
Purpose Control
- Verify whether data have been used for the intended purpose
- Auditing(查账, 审计, 审核; 审计学) Mechanism
- log data access and processing operations
- analyze logs to detect policy violations
Privacy as Control: Main characteristics
- Privacy is defined as the ability to specify acceptable data usage through
- policies defined by users(settings)
- policies defined by the organization
- Organizations are trusted to enforce policies
Privacy as Confidentiality: Assumptions
- Lack of transparency and data protection enforcement
- once data are under the control of an organization it is very difficult to verify how they are actually used
- abuse of personal information may not be evident to individuals
- Organizations that collect and process user data are not necessarily competent and honest, security is expensive
- Incentive to collect and use personal data for financial gain(without regard for user privacy)
- Large number of reported privacy breaches(Due to the lack of appropriate security practices)
- Placing high trust in organizations makes individual vulnerable(易受伤的, 脆弱的, 敏感的)
Privacy as Confidentiality: Threats
- Queries themselves are sensitive
- Inferred profiles(aggregated data)
- Linkability of user information across different contexts
- Identifiability: queries are hard to anonymize
- Massive collection of user information is considered in itself a privacy threat
- allow a variety of privacy violations: discrimination, manipulation, opportunistic abuse
- information asymmetries(不对称) reinforce power asymmetries: surveillance society
Privacy as Confidentiality: Goals
- Focus on minimal information disclosure
- Create an individual autonomous sphere free from intrusion
- Disclosure of information is BY DEFAULT prevented, or informaiton is minimally disclosed in a way that cannot be linked back to the individual
- individuals may still disclose information voluntarily
Anonymous credentials
- Based on zero-knowledge
- Prover can prove:
- he holds a credential with certain attributes, or
- any experession on them(simple arithmetic, boolean)e.g., age>18, gender=female
- Verifier gains no more information
- Applicaiton: E-cash
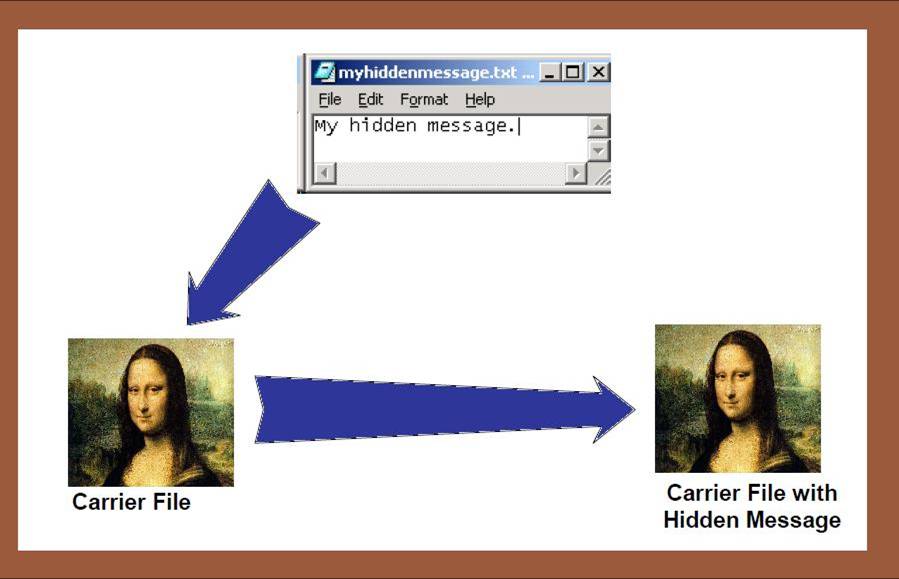
Steganography and Covert Communications
- Encryption: hide data content
- Anoymity/unlinkability: hide identities/relations
- Unobservability: hide existence
- Communications:
- Hide the fact that there is any communications
- Embed a communication within another
- Covert channels: hide secrets within public informationn
- Storage:
- Hide the existence of files
- Under coercion(强迫;强制;高压政治;威压) can deny there are any files to decrypt
Privacy as Confidentiality: Main Characteristics
- Privacy is defined as properities hard-coded in the technology itself
- Goal of technology is to ensure privacy properties hold
- Preventing data disclosure
- Minimize the need to trust others for handing sensitive data
Privacy as Practice: Assumptions
Transparency provide users with an understanding of the system
- Transparency produces awareness
- Awareness evokes actions
Privacy as Practice: Threats
Users has no means to know:
- which data are collected
- for which purpose his data are used
- how data are aggregated into profiles
- which decisions are made based on these profiles
Privacy as Practice: Goals
- Focus on user awareness
- Data collection is made transparent
- how, why, which data are collected
- users can intervene in the collection and use of data
- Data processing is made transparent
- discover undesirable privacy practices of organizations
P3P:Platform for Privacy Perferences
- Allow websites to communicate their privacy policies
- Provides a standard XML format to encode privacy policies
Help users understand privacy policies
NOTE: No enforcement!
Transparency Tools
- Give users a better understanding of information flow, state and history
- Become aware of how they (and others) participate in the socio-technical system
- Verify whether their personal privacy level fits within the current working of the system
- How they can take actions to change their own behavior as well as teh socio-technical environment
- Tools
- Google dashboard: see which info is associated to your account
- Fackbook: view how others see your profile
Privacy as Practice: Main characteristics
- Main objective is to support users in decision making
- Potential to uncover malicious behavior by organizations
Summary
| Control | Confidentiality | Practice | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Privacy definition:who fills the term privacy with meaning? | Organization-centric | Techno-centric | User-centric |
| Data Lifecycle | Information usage | Information disclosure/collection | Transparency in data disclosure, collection and use |
| Trust/adversary model | Organization trusted, individual untrusted | Powerful threat model, rigorous security analysis | No threat model |